
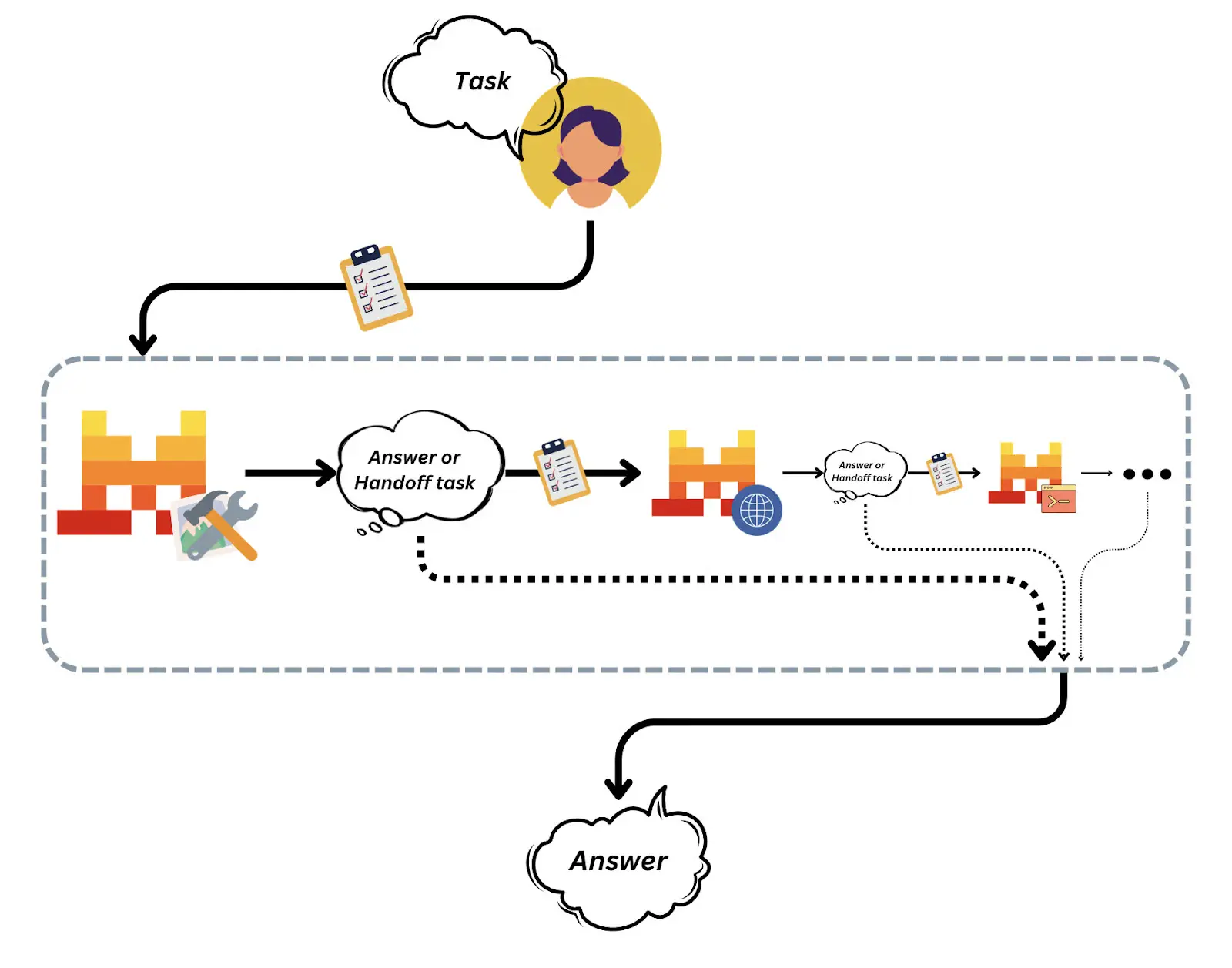
AI is shifting from single-shot prompts to agentic systems, autonomous software that can perceive its environment, reason about next steps, use tools, and keep working until the goal is met.
This isn't just hype. Teams across finance and operations are leveraging AI automation and agentic workflows to automate tasks, reduce overhead, and accelerate their processes. In this article, we will explore what AI agents are and provide 11 hands-on projects to help you get started and learn how to build AI agents. Each project comes with a complete AI agent tutorial to walk you through the build.
The projects are divided into three skill levels, ranging from beginners to advanced users:
- No-/Low-Code AI Agent Projects: For beginners who want to drag-and-drop their way to functional agents.
- API-Based AI Agent Projects: For developers who want more control, testing patterns, and production-ready practices.
- Agentic Framework Projects: For advanced builders tackling complex, multi-agent systems and orchestration.
What are AI Agents?
Imagine a team member who just gets things done. They understand the goals, gather the right info, pick the right tools, make informed decisions, and deliver impressive results. No handholding needed. That's essentially what an AI agent does, but in the digital world.
An AI agent is an autonomous system that uses large language models (LLMs) to perceive its environment, reason about it, and take purposeful actions to achieve specific goals. Unlike traditional bots or static automation, these autonomous AI systems can make independent decisions, solve problems flexibly, and collaborate dynamically across various tools, systems, and even with other agents.
What Makes AI Agents Different:
- Autonomy: Operate independently, making decisions and executing tasks without constant human oversight.
- Goal-Oriented: Pursue objectives set by users or systems, often breaking down complex goals into actionable steps.
- Perception & Reasoning: Gather and interpret data from APIs, web sources, or user input, and use LLMs to analyze, plan, and act.
- Tool Use: Integrate with external APIs, databases, and software to extend their capabilities.
- Adaptability: Learn from feedback and adjust to changing environments to improve over time.
- Collaboration: Work with other agents or humans in multi-agent systems to accomplish complex workflows.
What You'll Learn From These Projects
Working through these tutorials teaches you far more than just how to connect APIs or drag components around a canvas. You develop the architectural thinking that separates hobbyists from practitioners who can build systems that actually work in production.
-
Technical Foundations: You'll gain hands-on experience with the tools teams use to build real AI applications, from visual workflow builders like LangFlow to production frameworks like LangGraph and Google ADK. More importantly, you'll understand when each approach makes sense and how to combine different services into cohesive systems.
-
Systems Design: The projects progress from simple single-agent workflows to complex multi-agent orchestration. This teaches you how to structure data flows, handle errors gracefully, and design for scalability. You'll learn the difference between building a demo and building something reliable enough for others to depend on.
-
Practical Judgment: Perhaps most valuable is developing intuition about trade-offs. Should you use a no-code platform or write custom code? When does a single powerful agent work better than multiple specialized ones? How do you balance speed of development with control and customization? These questions only get answered through building real systems.
The deeper goal is bridging the gap between understanding AI concepts and actually implementing them. Many people can explain what agents are theoretically, but fewer can architect working systems that solve genuine problems. By the end of these projects, you'll have a portfolio demonstrating you can choose appropriate tools, structure complex workflows, and deploy applications others can actually use.
That said, the real learning comes from depth rather than breadth. Start with a couple of projects that match your current skill level and build them thoroughly, iterating and improving until they work reliably. This focused approach will teach you more than rushing through all of them quickly.
No-/Low-Code AI Agent Projects
These projects provide a great starting point for AI agent development for beginners and non-technical users. Instead of writing code, you can easily drag-and-drop components to create AI workflows.
Most platforms come with hundreds of ready-made templates, allowing you to load an example, insert your API keys, and plug in your data or knowledge base to start automating in minutes.
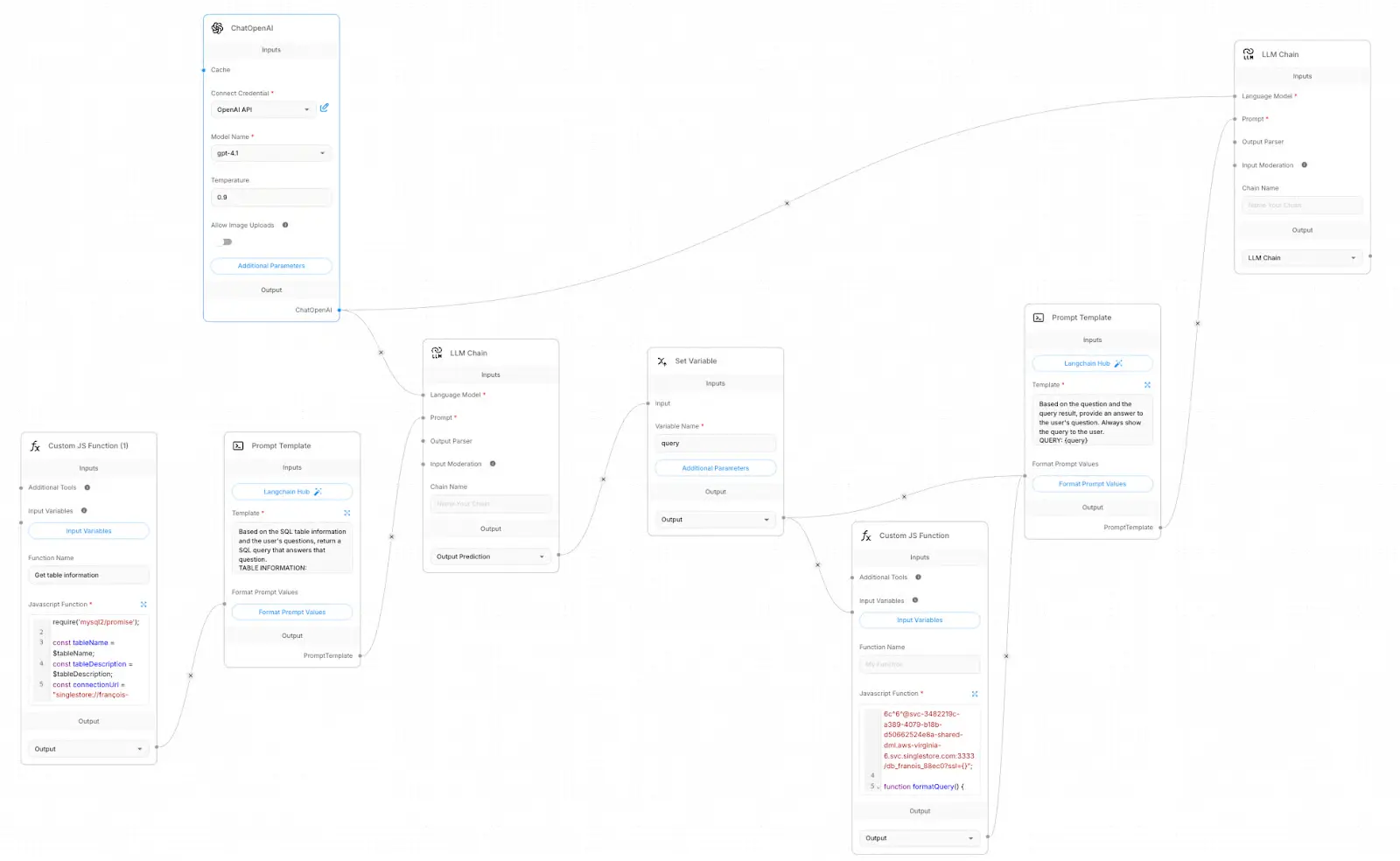
1. Data Analyst AI Agent with Flowise
The project guides you through transforming a CSV dataset into a conversational data analyst using Flowise's low-code, drag-and-drop workflow. You'll connect different blocks that read table metadata, translate natural language questions into SQL, execute queries against a SQL database, and return concise, readable answers using drag and drop AI workflows. Users simply ask questions about their data and get results.
This AI agent is great for internal analytics, data exploration, and lightweight BI prototypes. It's ideal for non-technical users who need quick, distraction-free insights from tabular data.
Guide: Flowise: A Guide With Demo Project
You'll gain hands-on experience in creating Flowise workflows with prompt templates, LLM chains, set-variable nodes, and custom code blocks. Additionally, you'll learn to design prompts for reliable text-to-SQL conversion, manage database connectivity and environment variables, execute queries and format results, and handle variables and error states across nodes.
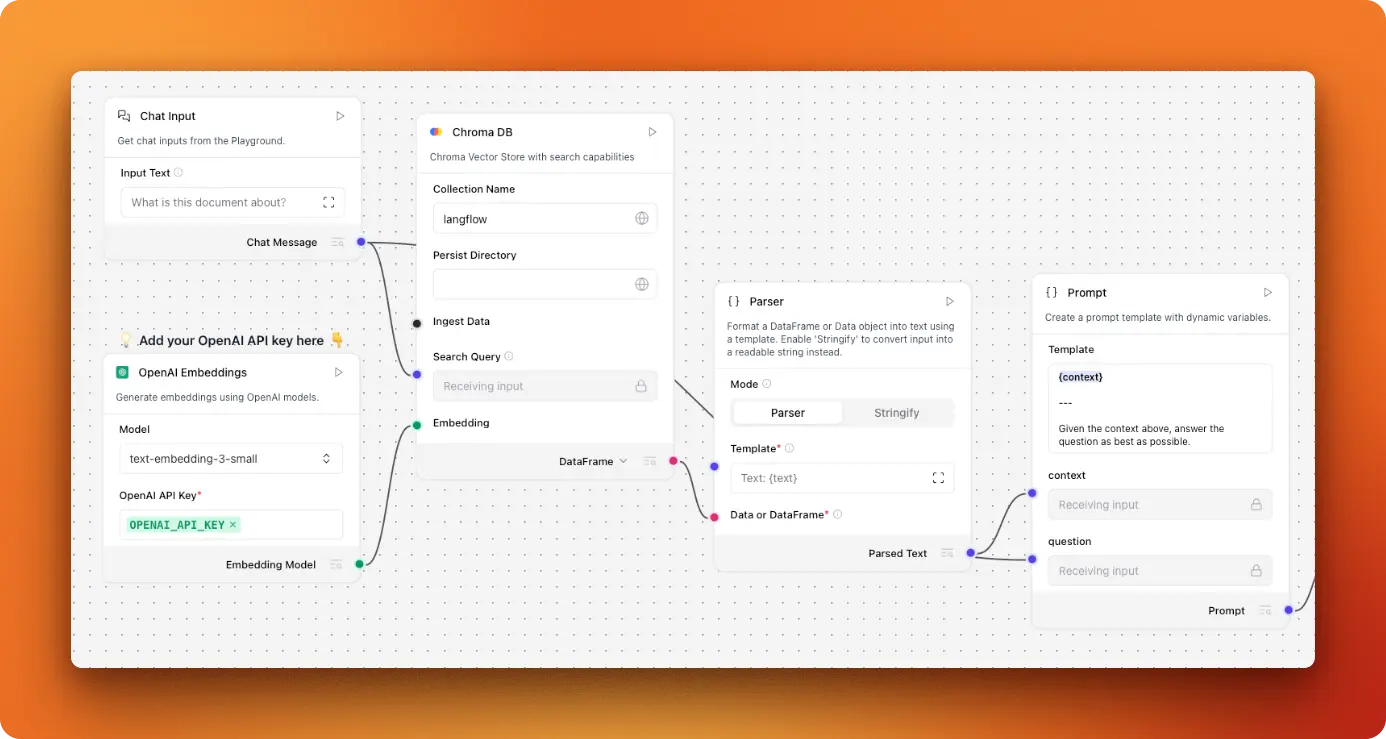
2. Build a PDF RAG System with LangFlow and Firecrawl
In this project, you'll turn a folder of PDFs into a conversational AI assistant you can talk to. You gather PDFs (or auto-convert web pages to PDF with Firecrawl), feed them into a visual RAG workflow in LangFlow, and then chat with them through a lightweight interface. It's meant for things like docs, manuals, and policies so people can ask questions and get grounded answers straight from the files.
Guide: Building a PDF RAG System with LangFlow and Firecrawl
You'll learn how to turn PDFs into searchable chunks, store them in a simple vector database, and wire everything together in a visual tool (LangFlow) without much code. You'll also practice writing clear prompts, building a tiny Streamlit chat app , handling messy files (OCR, odd layouts), adding metadata so answers can point back to pages, and doing basic debugging, error handling, and cost/speed tuning so the system feels fast and reliable.
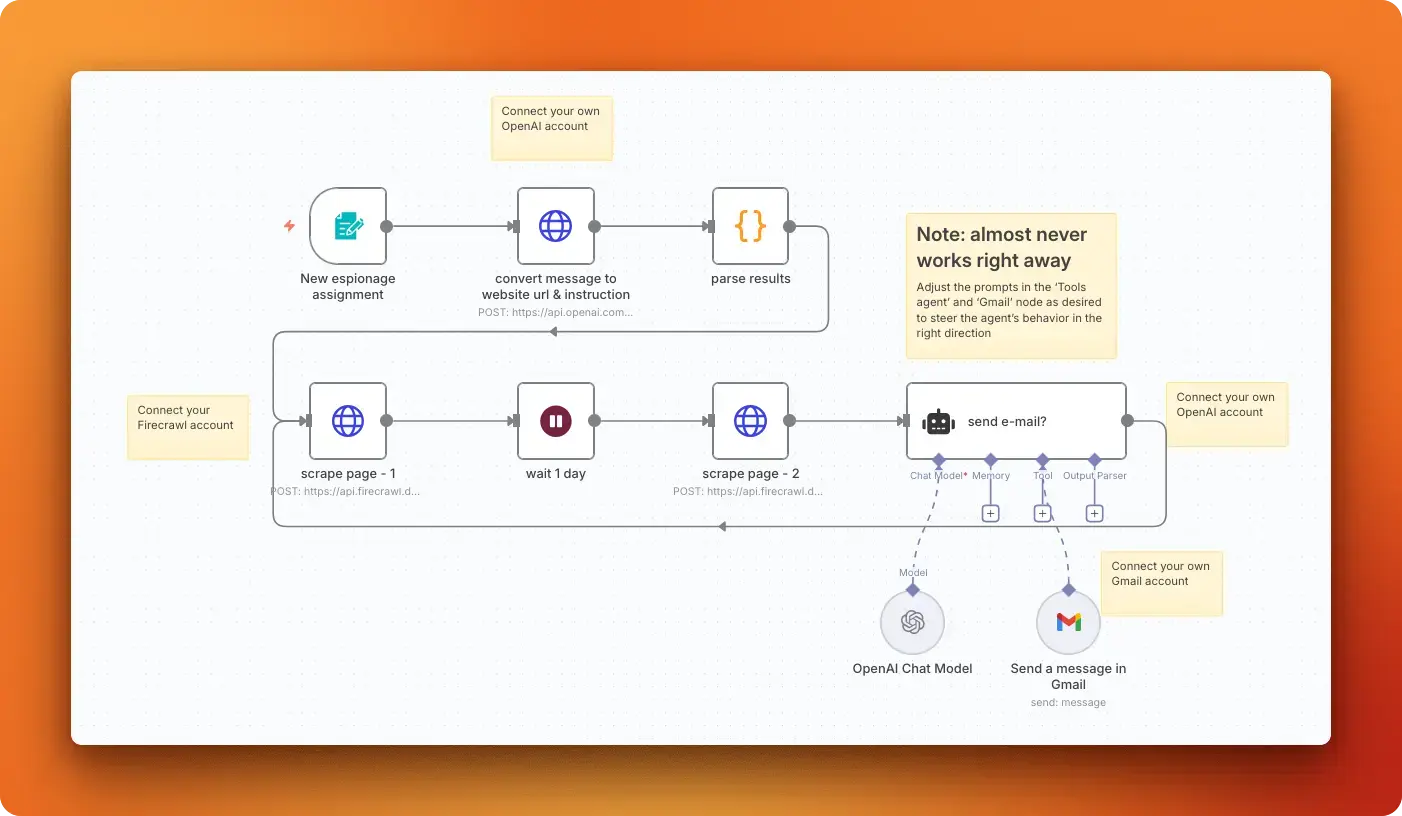
3. Competitor Website Monitoring with n8n
In this project, you'll set up a simple competitor website monitoring system that takes plain-English instructions (such as “monitor TechCorp's pricing page for price changes”) using a ready-made n8n template. The system will use an AI agent to identify the correct URL and the specific elements to watch for. It will scrape the site twice, approximately 24 hours apart, using Firecrawl, compare the two versions, and send a Gmail alert only when significant changes are detected.
Guide: Web Scraping with n8n: 8 Powerful Workflow Templates
By completing this project, you'll learn how to convert natural language requests into structured tasks with OpenAI, use Firecrawl's API to scrape the websites, schedule a 24-hour monitoring cycle, reliably compare content, employ AI agent (via LangChain) to filter for relevant changes, and send Gmail notifications.
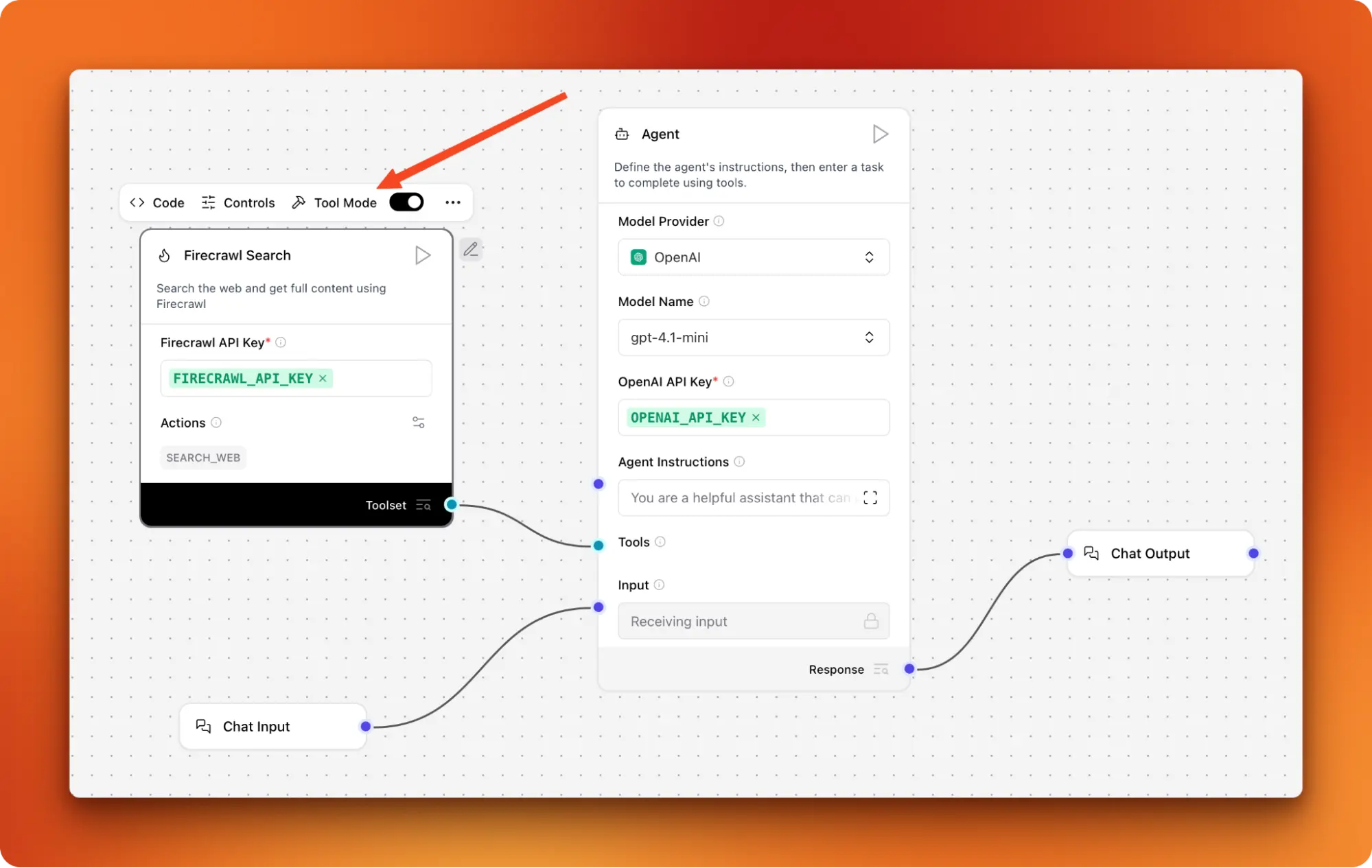
4. Building Production-Ready AI Apps with LangFlow
In this project, you'll use LangFlow's visual drag-and-drop builder to create an end-to-end AI agent with minimal coding. You'll start with a ready-made template (such as Document QA), connect inputs, prompts, and an OpenAI model, add a custom Firecrawl Search component for accessing live web content, and then expose your flow as a REST API or deploy it for others to use. The result is a complete AI application that can answer questions about documents while also searching the web for current information.
LangFlow automatically converts your visual workflow into a REST API that you can deploy anywhere. This means you can build sophisticated AI workflow automation without extensive coding knowledge, then deploy them as production-ready services that integrate with existing systems.
Guide: LangFlow Tutorial: Building Production-Ready AI Applications With Visual Workflows
This tutorial teaches you how to design and connect LangFlow components, manage inputs, outputs, and data types, write custom Python components, and integrate external APIs (Firecrawl). Additionally, you'll explore deployment options (self-hosted, Render, Railway, etc.) and practice comparing tools (LangFlow vs. Flowise, n8n, LangChain tutorial) to select the best approach for future projects.
API-Based AI Agent Projects
Ready to get your hands dirty? These projects give you more control without extensive coding. You can easily integrate an LLM API, which includes built-in function calling, agents, tools, and structured outputs, to quickly connect the necessary services for your agent. Many LLM providers now offer agent SDKs that allow you to build efficient agentic workflows using LLMs, tools, and prompts.
You might also be interested in reading our guide on LLM API Engine: How to Build a Dynamic API Generation Engine Powered by Firecrawl.
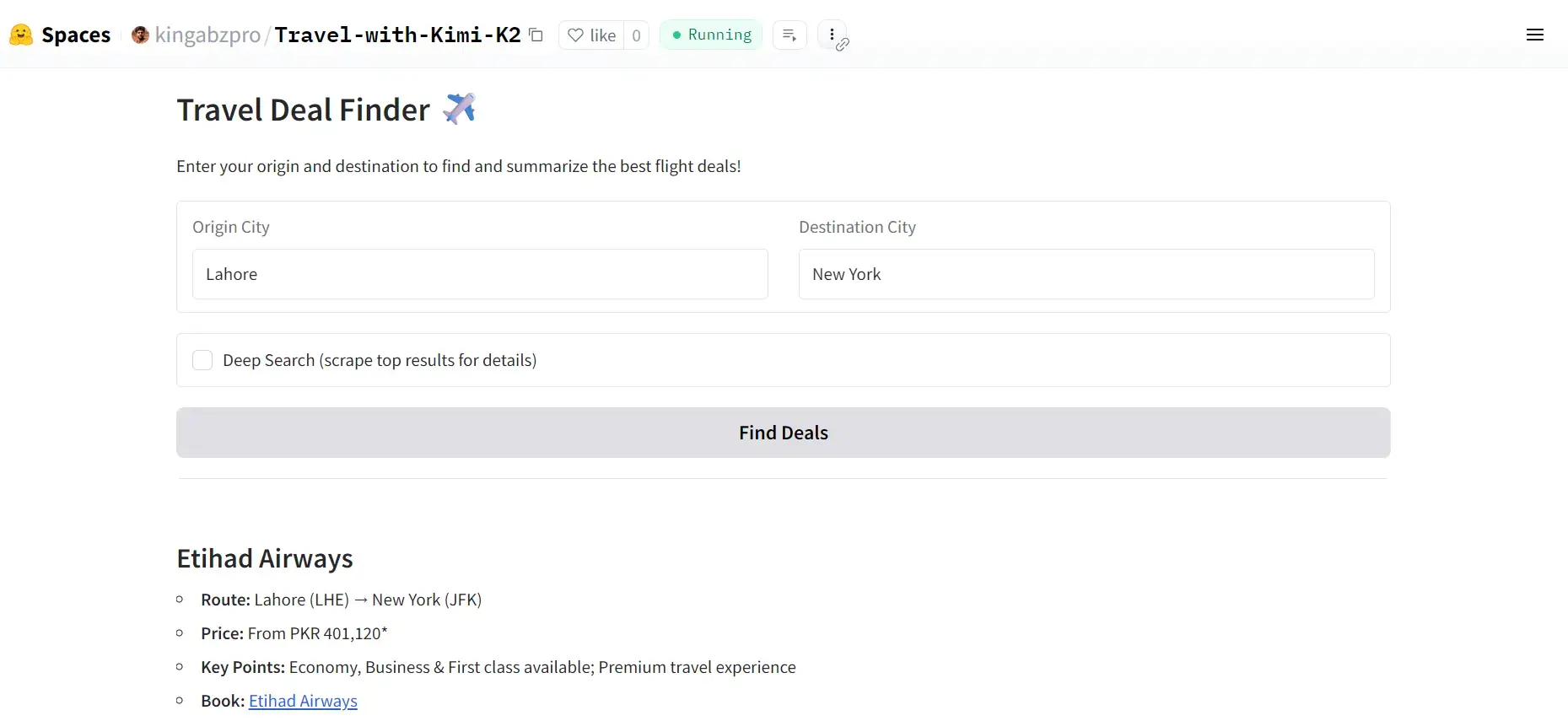
5. Travel Deal Finder using Kimi K2 and Firecrawl
This project builds a smart travel assistant that automates the tedious process of comparing flight prices across multiple airline websites. Instead of manually visiting different airline sites, the AI agent searches multiple sources simultaneously, extracts current pricing and availability, and presents everything in a clean, structured format with direct booking links.
The system uses Kimi K2 (via Groq) for intelligent processing and Firecrawl's web search API and scraping API, with a Gradio interface that makes it accessible to anyone. You can ask for flights between any cities and get real-time comparisons from major airlines like American, EVA Air, Singapore Airlines, and more.
At a high level, the project involves connecting the model to web search and scraping capabilities, routing the outputs into the user interface, and ensuring accessibility for users, emphasizing the flow of information rather than the technical mechanics.
Guide: Building AI Applications with Kimi K2: A Complete Travel Deal Finder Tutorial
Throughout the project, you practice transforming raw web content into structured, user-friendly summaries, coordinating the use of tools for search and scraping, and crafting prompts for an agentic large language model (LLM). You'll also explore basic UI design, secret management, lightweight deployment, and have a clear pathway to extend the project with agentic frameworks like LangGraph if you're interested in achieving greater autonomy and multi-step reasoning.
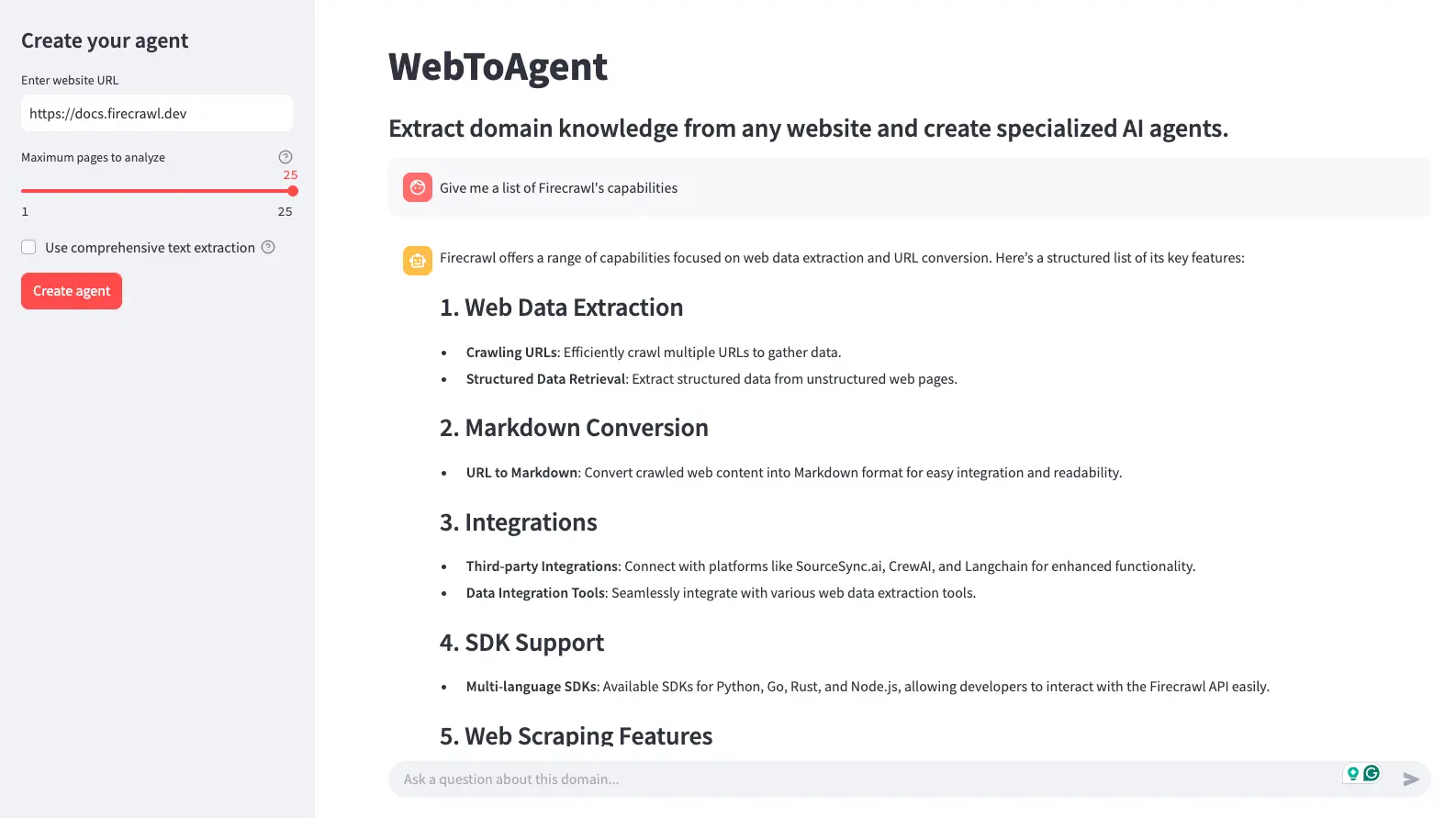
6. Turn Websites into Agents with OpenAI Agents SDK + LLMs.txt (Firecrawl)
This project demonstrates how to transform virtually any website into a conversational assistant by combining Firecrawl's LLMS.txt content extraction with OpenAI agents development.
The system extracts meaningful content from websites, structures it into organized knowledge (concepts, terminology, insights), then creates an agent that can answer questions about that specific domain. Users can chat with the agent to access information naturally, making websites more interactive and accessible than traditional search or browsing.
It involves setting up content extraction, defining a lightweight knowledge schema, creating an agent with clear instructions and output structure, and developing a compact interface that streams responses in real time. Instead of struggling with messy HTML, JavaScript, and navigation elements, you get clean, structured content that's ready for AI processing.
This agent is well suited for documentation, knowledge bases, and company websites where quick and distraction-free access to information is important.
Guide: Converting Entire Websites into Agents with Firecrawl's LLMs.txt Endpoint and OpenAI Agents SDK
You'll practice designing schemas for structured knowledge, orchestrating agent tools and model settings, handling asynchronous jobs and token streaming, managing configuration and environmental keys, and building a user-friendly chat interface with proper state management and error handling. Additionally, you'll gain experience in practical prompting, data validation using Pydantic, and iterative refinement of both content extraction and responses.
7. Nutrition Coach Agent with the Mistral Agents API
In this project, you'll create a simple AI Nutrition Coach using Mistral's Agents API. At a high level, you'll set up access, define a couple of lightweight agents and tools, and connect them in a brief workflow. This workflow can look up or estimate calories, log meals, suggest a subsequent dish, and optionally generate a relevant image. You can run the entire flow locally with a minimal user interface.
The app features a useful fallback system. If web search fails, it switches to AI-based calorie estimation. The whole workflow runs through a clean Gradio interface where you simply describe what you ate and get back calorie counts, meal logging confirmation, healthy suggestions for your next meal, and even a generated image to help you visualize it.
Guide: Mistral Agents API: A Guide With Demo Project
While building this project, you'll practice the fundamentals of agent-based app development, including composing system and user prompts, integrating built-in tools such as web search APIs and image generation, orchestrating multi-step interactions, safely parsing model and tool outputs, handling fallbacks and basic errors, organizing a small multi-file codebase, managing environment variables and API keys, and wrapping the pipeline in a simple interactive interface.
Agentic Framework Projects
These projects use advanced frameworks that require strong coding skills to customize how agents reason, plan, and act. With these frameworks, you are not just connecting APIs; you are engineering complete agentic workflows and even multi-agent systems that can communicate and collaborate to achieve complex goals.
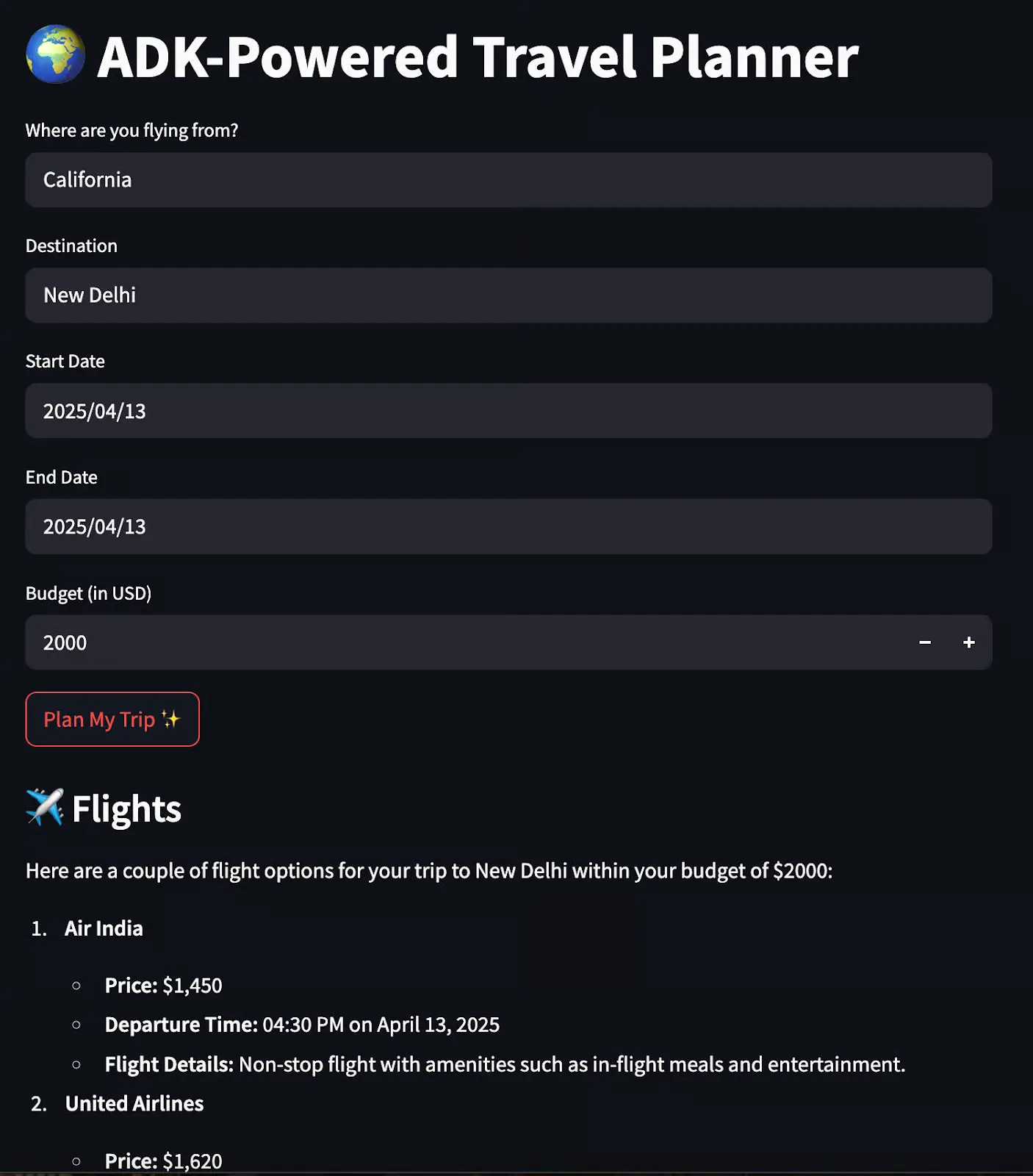
8. Travel Planner with Google ADK and A2A
In this project, you'll build a multi-agent travel assistant where specialized agents work together to plan complete trips, leveraging Google's Agent Development Kit (ADK). You'll create specialized agents for flights, accommodations, and activities, along with a host agent that coordinates everything. Each agent will run as a small FastAPI service that exposes a standard `/run` endpoint, and they communicate using Google's Agent-to-Agent (A2A) protocol over HTTP.
The system demonstrates true multi-agent architecture: when a user requests a trip to Paris, the host agent delegates to flight agents for transportation options, accommodation agents for places to stay, and activity agents for things to do. A Streamlit interface presents everything as a unified travel planning experience, even though multiple specialized services are working behind the scenes.
Guide: Agent Development Kit (ADK): A Guide With Demo Project
In this project, you'll learn how to define shared Pydantic schemas, make async REST calls with httpx, structure agents with ADK, coordinate multi-agent results, and return clean JSON to a UI. You'll also practice organizing service folders, adding basic logging/error handling, and wiring a Streamlit front end that calls the host agent and displays flights, stays, and activities.
9. Startup Idea Validator with LangGraph
In this project, you'll build a startup idea validator using LangGraph examples and a simple Streamlit chat user interface. The AI agent will take a business idea and perform a series of tasks: search the web with Firecrawl for market context, check Hacker News for community sentiment, and look at GitHub repositories to assess technical feasibility. Ultimately, it returns a clear and conversational assessment with recommendations.
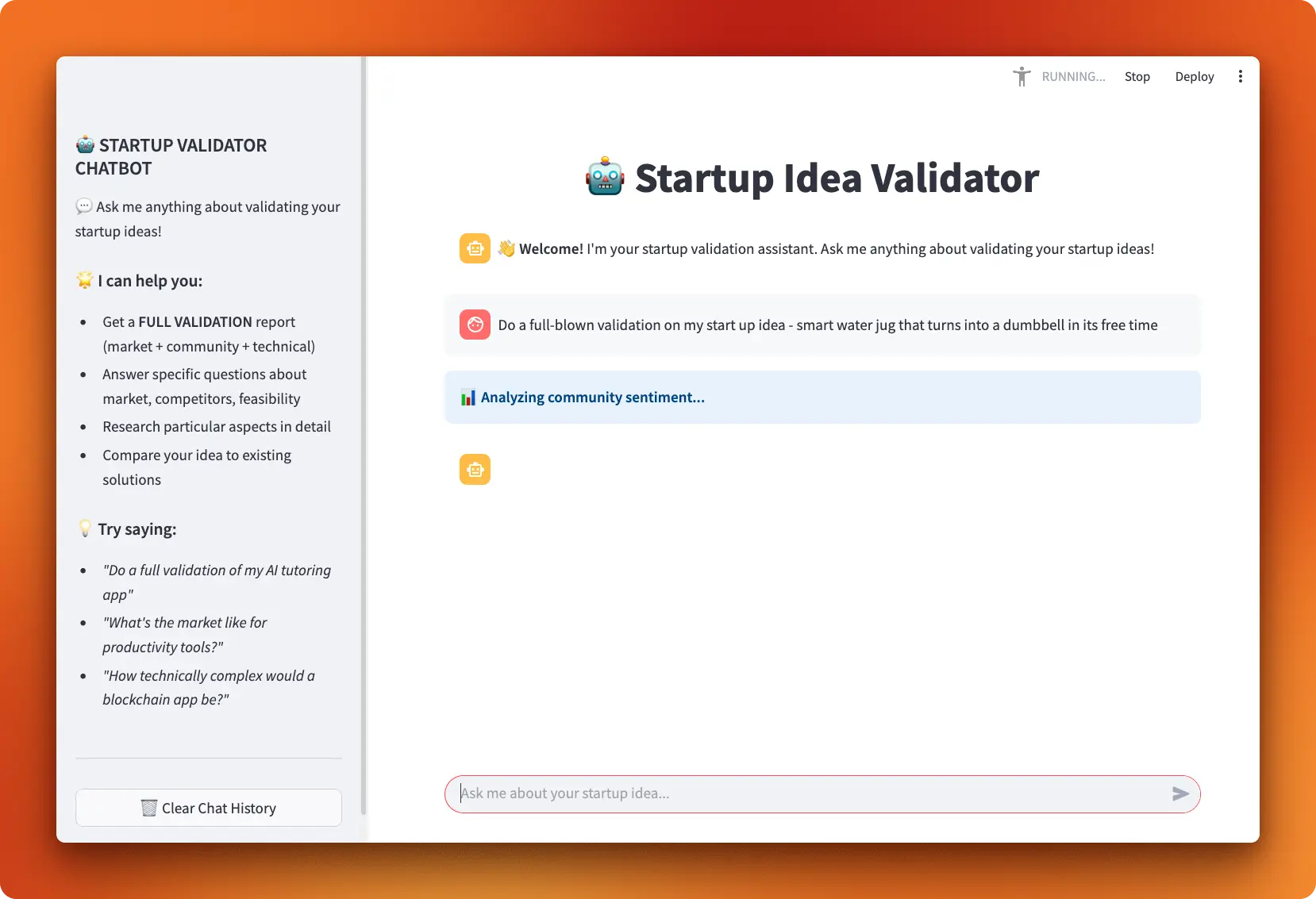
Guide: LangGraph Tutorial: Build a Startup Idea Validator with Interactive UI
With the project, you get hands-on experience integrating a LangGraph ReAct agent with various tools. You'll manage state and memory, call external APIs (including Firecrawl, HN Algolia, and GitHub), and write effective system prompts. Additionally, you'll learn how to stream progress and responses to the user interface, manage API keys, and implement basic error handling and fallbacks to ensure reliability.
10. Create Multi-Agent Applications with CrewAI
In this project, you'll build a multi-agent ChatGPT-style assistant using CrewAI projects. You'll begin by initializing the project, defining role-based agents and tasks, and integrating with Firecrawl's web search API. Next, you'll orchestrate everything within a crew and create a simple Streamlit UI, allowing users to interact with the system.
A crew is the coordinated group of role-based agents, their tasks, and tools that work together under one orchestration to achieve a shared goal.
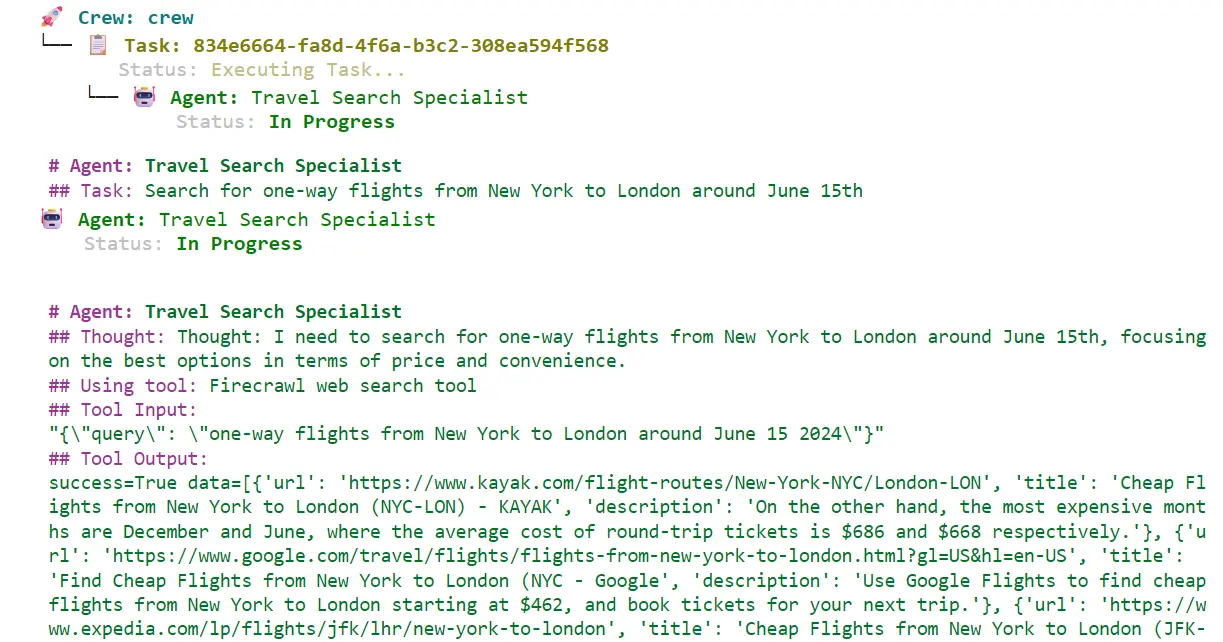
Guide: Building Multi-Agent Systems With CrewAI - A Comprehensive Tutorial
By completing this project, you'll learn how to configure agents and tasks in YAML, integrate and test custom tools, manage API keys, run and debug crews via the command line interface (CLI), handle structured outputs, and deploy a basic chat interface that calls your crew and displays responses.
11. Build a ChatGPT-Style Assistant with Google's ADK
This project creates a full-featured AI assistant that rivals commercial chatbots by combining multiple specialized agents into one unified interface, by using Google's Agent Development Kit (ADK). You'll set up the ADK project structure, create a main “chat” agent with specialized helpers, integrate Firecrawl for web search, scraping, and deep research, and add optional image generation capabilities.
The architecture uses specialized agents that work together: a search agent for real-time information, a web extraction agent for processing specific pages, a research agent for deep analysis, and an image generation agent for visual content. Users interact with a single interface while the system intelligently routes requests to the right specialist behind the scenes. The system will manage basic multi-agent orchestration, stream responses, and run locally so you can test the entire setup before considering deployment.
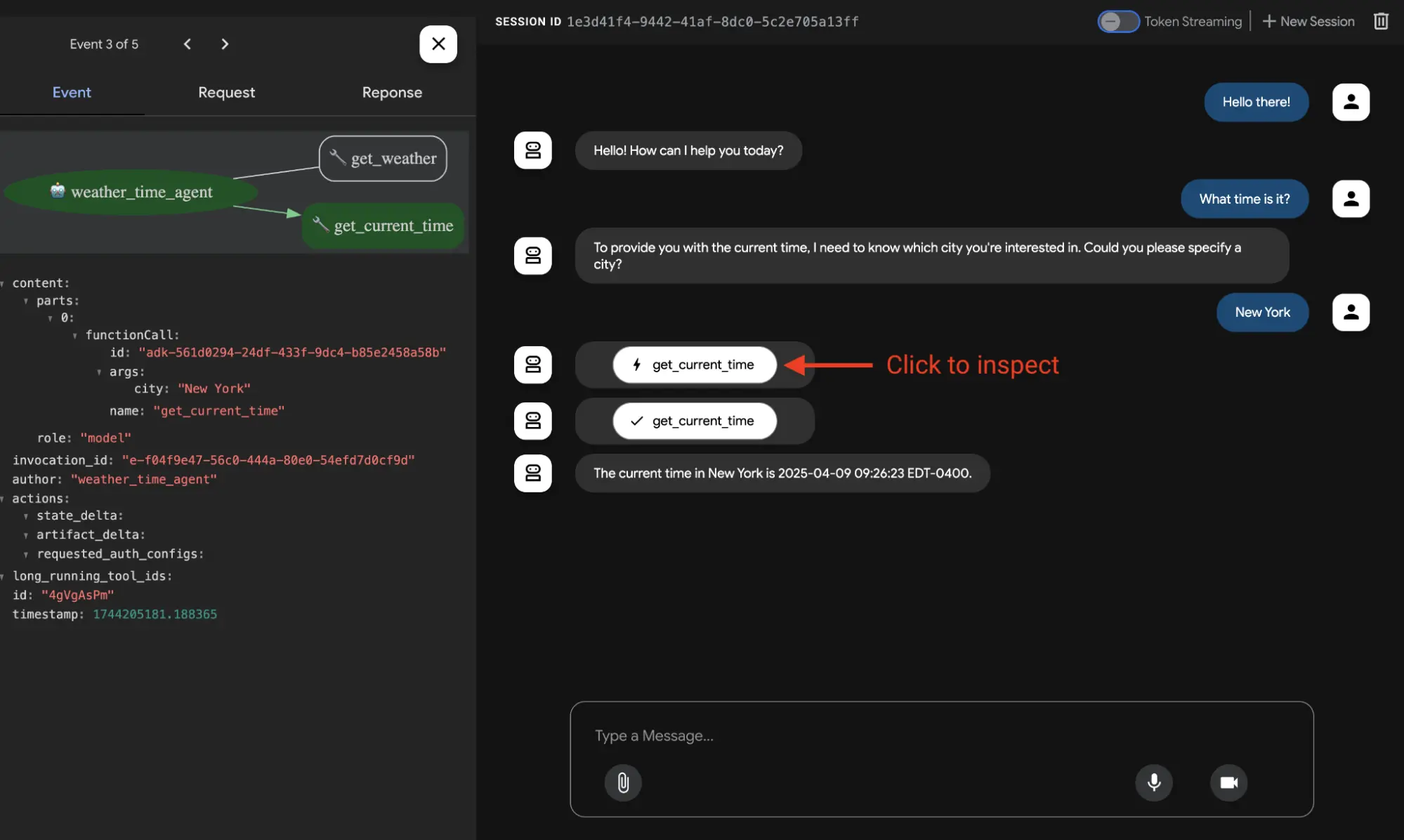
Guide: Comprehensive Guide to Building AI Agents Using Google Agent Development Kit (ADK)
By completing this project, you'll learn how to structure an ADK application, define agents and their roles, connect external tools like Firecrawl as capabilities, delegate tasks between agents, manage sessions and streaming, and implement basic safety checks.
How to Start Your Own AI Agent Project
Appraoaching these projects can seem daunting, but if you take it one step at a time, you'll be building your own production-ready AI Agent project in no time. Here's a run down on how to get started and what steps you need to follow in order to build your own production-ready AI Agent project.
- Understand the Fundamentals: Learn what AI agents are, how they perceive-reason-act, and the main build paths (no-/low-code, API-based, framework-based).
- Choose the Right Approach:
- Non-technical: No-/low-code (e.g., LangFlow, n8n).
- Developers: API-based builds with LLM SDKs.
- Experts: Agentic frameworks for full customization.
- Leverage Templates & SDKs: Jump-start with prebuilt templates and agentic SDKs; plug in API keys, connect tools, and prototype in minutes.
- Start Small & Iterate: Pick a single, high-value use case. Ship a minimal prototype, gather feedback, and expand step by step.
- Context Engineering for AI Agents: Provide the right information, in the right format, at the right time so agents can plan next steps effectively.
- Building Trustworthy AI Agents: Mitigate risks like prompt/goal injection, unauthorized access, service overloading, knowledge-base poisoning, and cascading errors.
- AI Agents in Production: Turn “black box” into a glass box with observability and evaluation. Evaluate quality, safety, tool-call success, latency, and cost.
- Multi-Agent Design Patterns: When complexity increases, use patterns like sequential, concurrent, or group chats to divide labor, parallelize work, and manage handoffs for intricate, cross-domain tasks.
- Engage With the Community: Don't go at it alone! Use forums, GitHub, and Discord to resolve issues, learn best practices, and stay current with rapidly evolving tools.
- Avoid Common Pitfalls: Don't over-engineer too soon. After all, these are for learning. Keep your agent's scope manageable, maintain user-centric design, and remember that simplicity scales better than complexity in the early stages.
Final Thoughts
I strongly believe that the best way to learn a new skill is through hands-on experience. Start by diving into a small project: break things, fix them, quickly search for solutions when you are stuck, read documentation, and keep building. This practical approach provides you with real-world experience and helps you build a stronger portfolio to showcase on your resume.
Begin with no/low-code tools to create simple AI agents. Test them and iterate on your designs. As you gain confidence, make your projects production-ready by incorporating basic software engineering practices such as version control, logging, error handling, testing, and monitoring. This will ensure your projects are reliable and low-maintenance.
Most LLM providers now offer APIs for agents that you can call directly and often at a low cost. To scale effectively, learn multiple agent frameworks and deployment strategies. You're now equipped to design reliable and scalable systems capable of handling high traffic with confidence.

data from the web